Climate Change and Its Impacts on Ecosystems and Human Societies
Climate change is a global issue that impacts ecosystems and human societies alike in numerous ways. It poses an imminent danger to all life on Earth – humans included – as well as animals, plants and microorganisms that inhabit them.
Climate change has the potential to drastically diminish access and quality of ecosystem services that people rely on for their livelihoods, food security, and protection from disasters and other threats. These include:
Ecosystems provide many essential resources, such as food, water, fuel, fibre, habitat and clean air; plus cultural and economic values (e.g. sense of place or appreciation of nature). Ecosystems play a pivotal role in producing these resources while also protecting them while providing many other ecosystem services.
Ecosystems play an essential role in maintaining the nutrient cycle, safeguarding against hazards and controlling climate. These activities have a major impact on people’s health and well-being.
At present, human activities account for more than 80% of total greenhouse gas emissions, with fossil fuel burning (coal, oil and natural gas) as the primary driver. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the principal greenhouse gas emitted into the atmosphere through human activity.
These emissions are altering the climate and ecosystem processes in unforeseen ways that remain poorly understood, but which could have long-lasting impacts.
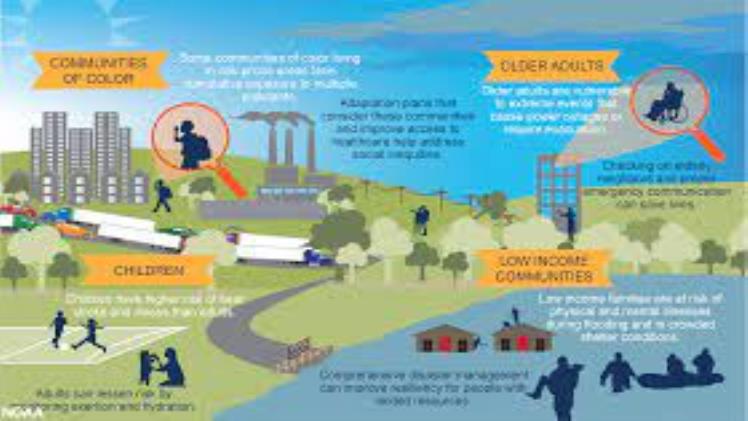
Climate change has the potential to have a devastating effect on human lives, compromising food security and causing flooding, extreme heat, infectious diseases, loss of agricultural land and natural resources as well as economic losses. As such, the World Health Organization has named climate change the greatest threat to global health in the 21st century.
Adaptation to climate change refers to the process by which humans and nature attempt to adjust in response to its effects. This may involve altering land-use patterns, using alternative fuel sources, or taking other actions.
However, there are challenges in implementing these adaptations. These could include energy costs, climate uncertainty and the requirement for large-scale infrastructure. Furthermore, benefits from a mitigation plan take time to materialize due to inertia in economic and climatic systems.
Therefore, adaptations must be implemented simultaneously with mitigation efforts. Doing this is crucial in order to keep warming on a lower trajectory and avoid the most devastating effects of climate change.
Climate change is becoming an increasingly pressing global issue, yet many lack understanding about its effects and how to adapt. This lack of awareness is especially prevalent in poorer and remote regions.
Climate change poses the potential risk that people may take unintended destructive and inefficient actions. This could result in weaker planning, increased violence and altered habits and personalities.
Climate change is already manifesting itself in the form of species extinctions and mass mortality events, particularly in polar regions and mountainous terrain. These tragedies are occurring at an unprecedented rate and will only become more frequent and severe as climates shift.